Air in brake lines is primarily caused by a leak or insufficient bleeding of the brake system. This results in a loss of hydraulic pressure, leading to air entering the lines.
When air is present in the brake lines, it can cause problems with brake performance, such as spongy or unresponsive brakes.
Ensuring proper maintenance and regularly checking for leaks can help prevent air from entering the brake lines and maintain optimal brake performance.
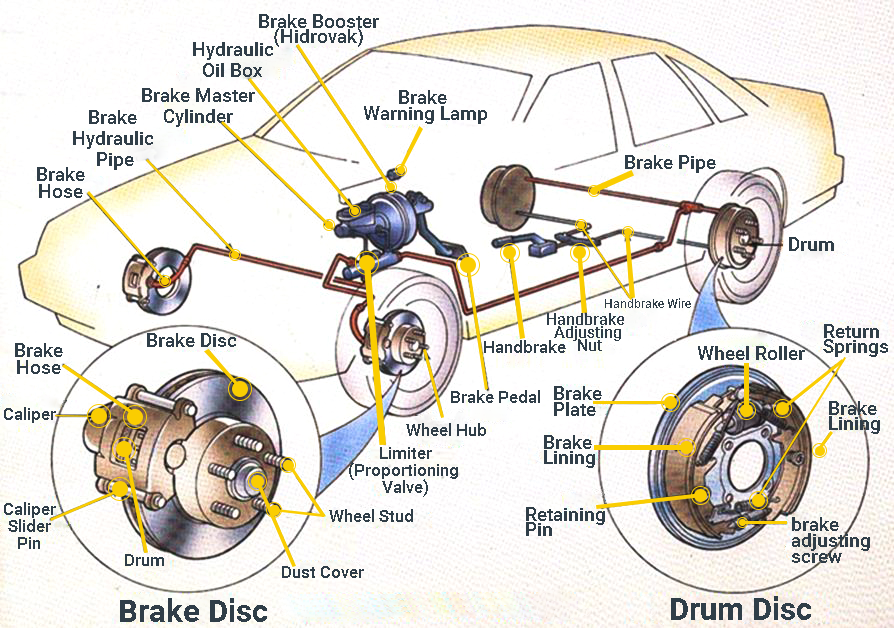
Credit: frendioriginal.com
What Does Air In Brake Lines Feel Like
Air in brake lines can feel spongy or soft, reducing the braking responsiveness of a vehicle. When pressing the brake pedal, it may sink down further than normal, and the brakes may not engage as quickly or effectively.
This can lead to a dangerous lack of control and should be addressed immediately by a qualified mechanic.
When it comes to air in brake lines, it’s important to understand how it feels and manifests in your vehicle’s braking system. Here, we will discuss the common signs and symptoms of air in brake lines.
Signs And Symptoms:
- Soft or spongy brake pedal: If you notice that your brake pedal feels soft or spongy, it could be a clear indicator of air in the brake lines. When air gets trapped in the brake lines, it creates a compressible pocket, leading to a loss of brake pedal firmness.
- Longer braking distance: Another tell-tale sign of air in the brake lines is the need for a longer braking distance. As air bubbles interfere with the flow of hydraulic fluid, the pressure required to apply the brakes increases, resulting in reduced braking efficiency.
- Brake pedal sinks to the floor: When air is present in the brake lines, you may experience a situation where the brake pedal sinks all the way to the floor when applying pressure. This occurs due to the presence of air occupying the space between the brake cylinder and the brake pads, preventing effective braking.
- Braking feels inconsistent: In the presence of air in the brake lines, you may also notice inconsistent brake performance. This means that sometimes the brakes may work fine, while at other times, they may feel weak or unresponsive. This inconsistency is due to the air impediment in the hydraulic system.
- Squealing or grinding noise: Air in the brake lines can create noisy brake operation. If you hear squealing or grinding noises while applying the brakes, it could be an indication that air bubbles are causing the brake pads to make improper contact with the rotors.
Understanding the signs and symptoms associated with air in brake lines is essential for promptly detecting and addressing this issue. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is recommended to have your vehicle inspected and the brake lines bled to remove any air.
How To Get Air Out Of The Brake Lines
Air in brake lines can be caused by a number of factors, including leaks, improper bleeding, or worn-out brake components.
To get air out of the brake lines, you need to properly bleed the system, ensuring all air bubbles are removed and only brake fluid remains.
This helps maintain smooth and effective braking performance.
Causes Of Air In Brake Lines
Air in brake lines can lead to decreased braking performance and potential safety hazards. Understanding the causes of air in brake lines is essential for maintaining the integrity of your vehicle’s braking system. Here are a few common reasons why air can get into the brake lines:
Worn Or Damaged Brake Components:
- Brake hoses, calipers, or master cylinders with leaks can introduce air into the brake lines.
- Damaged or worn rubber seals in the brake system can allow air to enter.
Improper Brake Bleeding:
- Inadequate brake bleeding during brake system maintenance can cause air pockets to remain in the lines.
- Failing to follow the proper sequence while bleeding the brakes can also result in air in the system.
Failing Brake Components:
- A failing master cylinder or brake booster can introduce air into the brake lines.
- Old or worn-out brake pads can cause excessive heat in the system, leading to air accumulation.
Removing air from brake lines requires a systematic approach to ensure proper braking performance. Here are some methods to help get air out of the brake lines:
- Prepare the vehicle:
- Park the vehicle on level ground and engage the parking brake.
- Ensure that the brake fluid reservoir is filled to the recommended level.
- Gather the necessary tools:
- Brake bleeder wrench or appropriate-size wrench for brake bleed screws.
- Clear plastic tubing to attach to the brake bleed screws.
- A container to collect the old brake fluid.
- Start with the wheel farthest from the master cylinder:
- Loosen the brake bleed screw on the caliper or wheel cylinder.
- Attach the clear plastic tubing to the bleed screw and place the other end into the container.
- Have an assistant slowly depress the brake pedal and hold it down.
- Begin the bleeding process:
- Open the brake bleed screw and allow the brake fluid to flow through the tubing.
- Once the fluid flow stops, close the bleed screw before releasing the brake pedal.
- Repeat the process:
- Continue bleeding each brake caliper or wheel cylinder, working from the farthest to the nearest to the master cylinder.
- Ensure that the brake fluid reservoir is topped up during the bleeding process.
- Check and adjust brake fluid level:
- Once you have bled all the brake lines, check the brake fluid level in the reservoir.
- Top up if necessary, using the recommended brake fluid.
By following these steps, you can effectively remove air from the brake lines and restore optimal braking performance to your vehicle.
Remember to take appropriate safety precautions and consult a professional if you are unsure about the brake bleeding process.

Credit: m.youtube.com
Conclusion
Air in brake lines can be caused by various issues such as worn-out seals, leaking connections, or low brake fluid levels. It is essential to regularly maintain the brake system to prevent air from entering the lines.
Proper maintenance and prompt repairs of brake issues can help ensure a safer and more reliable driving experience.
